Content
- Public Company Audit Services
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- What Is The Difference Between Loan Payable And Loan Receivable?
- Want More Helpful Articles About Running A Business?
- Jumbo Loan
- How To Record A Note Payable With No Cash Deposit
- Amortization
- Loan Extended And Expected Cash Flows To Be Received Later Than Forecast
This does not include money paid, it is only the amounts that are expected to be paid. Let’s say that $15,000 was used to buy a machine to make the pedals for the bikes. That machine is part of your company’s resources, an asset that the value of such should be noted. In fact, it will still be an asset long after the loan is paid off, but consider that its value will depreciate too as each year goes by. RSM US LLP is a limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of RSM International, a global network of independent audit, tax and consulting firms. 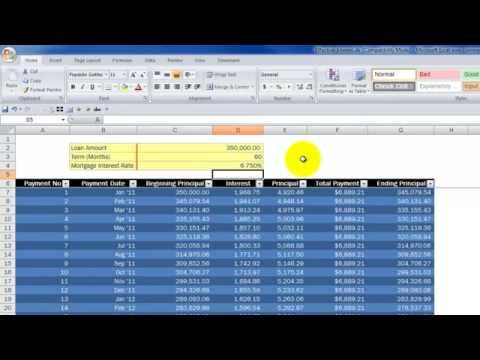
Public Company Audit Services
A company may owe money to the bank, or even another business at any time during the company’s history. (This is caused by a net ½ percent fall in market interest rates at a 4 to 1 tradeoff between interest rate and discount points.) Thus, the institution earned its targeted margin of $1,500 or 1.50%. If there is no immediate loan repayment, with only interest being paid, then the entry is a debit to the interest expense account and a credit to the cash account. The bank will record the loan by increasing a current asset such as Loans to Customers or Loans Receivable and increasing a current liability such as Customer Demand Deposits. Interest expense is calculated on theoutstanding amountof loan during that period, i.e. the unpaid principal amount outstanding during the period. 
Mortgage Amortization Calculator
The institution records $5,000,000 of loans receivable and an overall contra account of $1,586,790. Loan loss provisions are added to the loan loss reserves, a balance statement item showing total loan losses. To record a periodic loan payment, a business first applies the payment toward interest expense and then debits the remaining amount to the loan account to reduce its outstanding balance. Interest payments sometimes are made after the interest is accrued and recorded. In this case, making an interest payment does not cause a business to incur interest expense again.After 2 years, the liability will be re-classified under current liabilities, i.e. when the loan is due to be settled within one year. Accounting for loan payables, such as bank loans, involves taking account of receipt of loan, re-payment of loan principal and interest expense. If you are the company loaning the money, then the “Loans Receivable” lists the exact amounts of money that is due from your borrowers.
What is the double entry for a loan?
The double entry to be recorded by the bank is: 1) a debit to the bank’s current asset account Loans to Customers or Loans Receivable for the principal amount it expects to collect, and 2) a credit to the bank’s current liability account Customer Demand Deposits.In the first month, $75 of the $664.03 monthly payment goes to interest. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace. This means the amount is deducted from the bank’s cash to pay the loan amount out to you.
What Is The Difference Between Loan Payable And Loan Receivable?
Our first step is to reverse the additional loan loss reserve of $5,980 (Appendix E-I, col 19) that we recorded in Quarter 1 (Appendix E-I, col 23). We are still left with the new present value of the cash flows exceeding the carrying amount by $4,434.
How do you record transactions in a cash book?
Just like cash transactions, all payments into the bank are recorded on the left side and all withdrawals/payments through the bank are recorded on the right side. When cash is deposited in the bank or cash is withdrawn from the bank, both the entries are recorded in the cash book.He has written for goldprice.org, shareguides.co.uk and upskilled.com.au. Way holds a Master of Business Administration in finance from Central Michigan University and a Master of Accountancy from Golden Gate University in San Francisco.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running A Business?
Amortization is important because it helps businesses and investors understand and forecast their costs over time. In the context of loan repayment, amortization schedules provide clarity into what portion of a loan payment consists of interest versus principal. This can be useful for purposes such as deducting interest payments for tax purposes. Amortizing intangible assets is also important because it can reduce a business’ taxable income and therefore its tax liability, while giving investors a better understanding of the company’s true earnings.
- Accelerated amortization occurs when a borrower makes extra payments toward their mortgage principal, speeding up the settlement of their debt.
- If you are the company loaning the money, then the “Loans Receivable” lists the exact amounts of money that is due from your borrowers.
- We believe the fair value determination should be based on the gain or loss that would occur if the institution were to pair-off the transaction with the investor at the measurement date.
- A higher percentage of the flat monthly payment goes toward interest early in the loan, but with each subsequent payment, a greater percentage of it goes toward the loan’s principal.
- 1-4 family residential mortgage loans held for sale at quarter-end are reported on 4a.
- The difference between a loan payable and loan receivable is that one is a liability to a company and one is an asset.
The RC-Q threshold for other liabilities is $25,000 and 25 percent of the total amount reported on RC-L 9. In the case where a financial institution has elected to account for its best efforts commitment at fair value, it must report the following. We believe the fair value determination should be based on the gain or loss that would occur if the institution were to pair-off the transaction with the investor at the measurement date. IRLCs with positive values may not be offset against the IRLCs with negative values when presenting assets and liabilities on the statement of financial condition. Following is an accounting example for our $100,000 loan from inception to loan closing or funding. In prior guidance, the origination costs were also not amortized. Like the change in the value of the IRLC, the costs were accounted for as an adjustment to the basis of the loan at closing.
Jumbo Loan
In addition, we have disclosed remaining term in months , the remaining amortization term, the coupon rate , and the accretion rate used during the quarter. We recommend that future cash flows be calculated based on weighted averages only when the underlying loans have very similar terms and payment structures, such as for a group of auto loans. For loans within a pool that have varying lives and payments, such as residential mortgages, we recommend projecting the cash flow for each loan and then aggregating those cash flows into one pooled asset. This way the overall life of the pooled loans will still reflect the characteristics of the underlying loans, and the time period for the accretion will be correct. Despite these improvements, banks still have to account for loan defaults and expenses that occur as a result of lending. Loan loss provisions are a standard accounting adjustment made to a bank’s loan loss reserves included in the financial statements of banks. Loan loss provisions are consistently made to incorporate changing projections for losses from the bank’s lending products.This financial position is often released publicly through the bank’s quarterly financial statements. Unamortized loans are repaid at once in the amount of the loan principal at maturity. To record the loan payment, a business debits the loan account to remove the loan liability from the books, and credits the cash account for the payment. For an amortized loan, payments are made over time to cover both interest expense and the reduction of the loan principal.A loan loss provision is an income statement expense set aside to allow for uncollected loans and loan payments. If a loan is amortized, the recording must reflect changes in outstanding loan balance over the loan term. This would require periodic adjustments to the original loan principal. The accounts used to record a loan in bookkeeping consists of different liability accounts, an interest expense account and the cash account. If market rates increase, the fair value of the forward sales contracts has increased and the value of the loan has decreased. The fair value of the loan and the contract are based on market prices.The amount is listed here under this liability account, showing that the amount is to be paid back. Member firms of the KPMG network of independent firms are affiliated with KPMG International. © 2021 Copyright owned by one or more of the KPMG International entities. Since the last time you logged in our privacy statement has been updated. We want to ensure that you are kept up to date with any changes and as such would ask that you take a moment to review the changes. You will not continue to receive KPMG subscriptions until you accept the changes.Accelerated amortization occurs when a borrower makes extra payments toward their mortgage principal, speeding up the settlement of their debt. A loan amortization schedule is a complete schedule of periodic blended loan payments showing the amount of principal and the amount of interest. Amortizing intangible assets is important because it can reduce a business’ taxable income, and therefore its tax liability, while giving investors a better understanding of the company’s true earnings. Amortization can refer to the process of paying off debt over time in regular installments of interest and principal sufficient to repay the loan in full by its maturity date. A higher percentage of the flat monthly payment goes toward interest early in the loan, but with each subsequent payment, a greater percentage of it goes toward the loan’s principal. General provisions are balance sheet items representing funds set aside by a company as assets to pay for anticipated future losses. If the debt is in the form of a credit card statement, this is typically handled as an account payable, and so is simply recorded through the accounts payable module in the accounting software.The total amount of gains and losses must be included on RI Memoranda 13a and RI-13b. Information regarding forward contracts must be included in the financial institution’s call report. The table below shows the change in the value of the IRLC as market interest rates and estimated pull through percentages change over time.
Amortization
1-4 family residential mortgage loans held for sale at quarter-end are reported on 4a. 1-4 family residential mortgage loans sold during the quarter are reported on 3 a. Similarly, we believe the appropriate uncommitted loan prices are Level 2 inputs as well. There may be an overall gain or loss depending on the economic effectiveness of the forward sales contracts as a hedge, since both the loans and the forward sales commitments are marked to market separately. Our ending carrying amount is equal to the beginning principal balance of $5,000,000 reduced by the $45,878 of principal received less the new contra account balance of $1,534,611. We note that not only is it important to estimate theamountof the future cash flows, it is also important to estimate thetimingof the future cash flows.When recording a loan in bookkeeping, a business must accrue the interest expense on the same periodic basis even if the interest is not currently due. The accrued interest is debited to the interest expense account and a credit is made to a current liability account under interest payable for the pending interest payment liability. Noninterest income for the quarter from loan sales and servicing of 1-4 family residential mortgage loans is reported on 5a. This asymmetrical accounting resulting from decrease in market interest rates has led some institutions to elect hedge accounting for their closed loan inventory.The IRS has schedules that dictate the total number of years in which to expense tangible and intangible assets for tax purposes. An FHA 203 loan provides money for purchases, repairs, and other related expenses for individuals who want to buy and rehabilitate a damaged home. Bad debt is an expense that a business incurs once the repayment of credit previously extended to a customer is estimated to be uncollectible. The lender agrees to lend funds to the borrower upon a promise by the borrower to pay interest on the debt, usually with the interest to be paid at regular intervals. A person or business acquires debt in order to use the funds for operating needs or capital purchases. Let’s assume that a company obtains a $30,000 bank loan that must be repaid within 9 months. The bank deposits the loan proceeds of $30,000 into the company’s checking account at the same bank.
