Content
- Accountingtools
- What Are Investing Activities In Accounting?
- Cash Flows From Investing Activities Definition
- What Are Cash Flows From Investing Activities?
- Free Accounting Courses
- Business In Action 12 2
Types of activities that this may include are capital expenditures, lending money, and sale of investment securities. Along with this, expenditures in property, plant and equipment fall within this category as they are a long-term investment. Cash flow from investing activities is stated on the cash flow statement. To determine cash flows from investing activities, the accountant must analyze the changes that have taken place in each nonoperational asset such as buildings and equipment. Journal entries can be recreated to show the amount of any cash inflow or cash outflow.
Can you really make money buying stocks?
Three ways to make money in the stock market are: Sell stock shares at a profit—that is, for a higher price than you paid for them. … Short-selling is a bet that a stock will decline in value. Collecting dividends—Many stocks pay dividends, a distribution of the company’s profits per share.When a company purchases a new vehicle withcash, the cash outflows are listed in the investing section. Likewise, if a company sells one of its vehicles, the cash proceeds are listed in this section as well. Investing activity is an important aspect of growth and capital. A change to property, plant, and equipment , a large line item on the balance sheet, is considered an investing activity. When investors and analysts want to know how much a company spends on PPE, they can look for the sources and uses of funds in the investing section of the cash flow statement. Spending this amount to settle a $204,000 liability does create the $25,000 reported loss. This cash outflow of $229,000 relates to a liability and is thus listed on the statement of cash flows as a financing activity.
Accountingtools
The procedures used in determining cash amounts to be reported as financing activities are the same as demonstrated for investing activities. The change in each nonoperating liability and stockholders’ equity account is analyzed. The recording of individual transactions can be replicated so that the cash effect is isolated. Analyze the changes in nonoperational liabilities and stockholders’ equity accounts to determine cash inflows and outflows from financing activities.The two main activities that fall in the investing section are long-term assets and investments. Long-term assets usually consist of fixed assets like vehicles, buildings, and machinery. 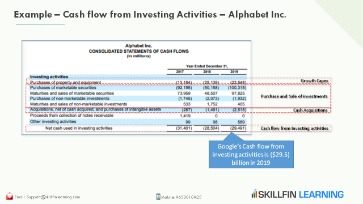
What Are Investing Activities In Accounting?
Instead, they fall into the category of cash flow from operating activities. If a company is reporting consolidated financial statements, the preceding line items will aggregate the investing activities of all subsidiaries included in the consolidated results. As with any financial statement analysis, it’s best to analyze the cash flow statement in tandem with the balance sheet and income statement to get a complete picture of a company’s financial health.
- Financial statements are written records that convey the business activities and the financial performance of a company.
- David Kindness is a Certified Public Accountant and an expert in the fields of financial accounting, corporate and individual tax planning and preparation, and investing and retirement planning.
- The direct method of preparing a cash flow statement results in a more easily understood report.
- Consider a hypothetical example of Google’s net annual cash flow from investing activities.
- Investing activities include purchases of physical assets, investments in securities, or the sale of securities or assets.
For example, a potential investor can see that officials chose to spend cash of almost $1.6 billion during this year in connection with Disney’s parks, resorts and other property. Interestingly, this expenditure level is almost exactly the same as the monetary amount invested in those assets in the previous year. With knowledge of financial accounting, a portrait of a business and its activities begins to become clear. A section of the statement of cash flows that includes cash activities related to net income, such as cash receipts from sales revenue and cash payments for merchandise. You can find capital expenditure figures in the cash flow section of investment activities. An increase in capital expenditure indicates a company is investing in future operations. Although capital spending represents cash outflows, analysts often see companies with a significant amount of capital expenditure in a state of growth.For example, cash paid for short-term investments liketrading securitiesandcash equivalentsare included in this section. However, payments on a note payable from a customer that resulted in a sale are typically listed in theoperating activitiessection—not the investing. Likewise,FASBrequires that all interest payments and receipts be classified as operating activities. Cash flow from investing activities is important because it shows how a company is allocating cash for the long term. For instance, a company may invest in fixed assets such as property, plant, and equipment to grow the business. While this signals a negative cash flow from investing activities in the short-term, it may help the company generate cash flow in the longer term.Cash flow from financing activities is a section of a company’s cash flow statement, which shows the net flows of cash used to fund the company. Overall, the cash flow statement provides an account of the cash used in operations, including working capital, financing, and investing. There are three sections–labeled activities–on the cash flow statement. IAS 7 allows interest paid to be included in operating activities or financing activities. US GAAP requires that interest paid be included in operating activities.
Cash Flows From Investing Activities Definition
It involves buying and selling long-term assets and other business investments. When adding a new machine, for example, the company can produce more output. Likewise, with acquisitions, it makes a company more efficient or increases revenue. Cash flow from investing activities reports the total change in a company’s cash position from investment gains/losses and fixed asset investments. The indirect method uses net-income as a starting point, makes adjustments for all transactions for non-cash items, then adjusts from all cash-based transactions. An increase in an asset account is subtracted from net income, and an increase in a liability account is added back to net income. This method converts accrual-basis net income into cash flow by using a series of additions and deductions. 
What Are Cash Flows From Investing Activities?
All the sources and uses of this company’s cash are apparent from this schedule. Determining the cash amounts can take some computation but the information is then clear and useful. Cash of $400,000 was borrowed by signing a note payable with a local bank. Maybe we lend money to another company or collect money on a loan we previously gave .Notice how every year the company has “Investments in Property & Equipment,” which are its capital expenditures. There are no acquisitions (“Investments in Businesses”) in any of the years; however, it is there as a placeholder. Business activities are activities a business engages in for profit-making purposes, such as operations, investing, and financing activities. Below is the cash flow statement from Apple Inc. according to the company’s 10-Q report issued on June 29, 2019.
Free Accounting Courses
According to the information provided, another asset was acquired this year but its cost is unavailable. Once again, the accountant must puzzle out the amount of cash involved in the transaction.International Accounting Standard 7 is the International Accounting Standard that deals with cash flow statements. It is particularly important in capital-heavy industries, such as manufacturing, that require large investments in fixed assets. The direct method for creating a cash flow statement reports major classes of gross cash receipts and payments. Under IAS 7, dividends received may be reported under operating activities or under investing activities. Cash flow from investing activities is the cash that has been generated on non-current assets that are intended to produce a profit in the future.The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. The financial statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. Any changes in the cash position of a company that involves assets, investments, or equipment would be listed under investing activities.So even though the truck goes to the balance sheet, we need to note the entire purchase price on our cash flow statement. Operating activities are about how companies make money from the supply of goods and services. Investment activities are about how to grow a business and make more money in the future. Investment can be through the purchase of new machines or acquisitions, and both require payment. And financing such investments, for example, by issuing shares or bonds, is a cash flow component of financing activities. Capital expenditures , also found in this section, is a popular measure of capital investment used in the valuation of stocks. An increase in capital expenditures means the company is investing in future operations.This figure represents the amount of cash a company spent on items that last a long time, such as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Basically, capital expenditures–often referred to as “capex”–are brick-and-mortar types of investments that are necessary to keep the company running and growing in its current form. For example, in order for a supermarket to keep operating and growing, it will typically need to remodel its existing stores, replace its equipment, and build new stores. These expenditures will show up in the capex line item in the “cash flows from investing activities” section.In collective, the cash spending on the investment of capital assets refers to as capital expenditure. Investments in highly liquid securities are excluded from investing activities. Therefore, buying and selling activities of cash equivalents that are highly liquid and securities for trading purposes are not part of investment activities.Consider a hypothetical example of Google’s net annual cash flow from investing activities. For the year, the company spent $30 billion on capital expenditures, of which the majority were fixed assets. Along with this, it purchased $5 billion in investments and spent $1 billion on acquisitions. The company also realized positive inflow of $3 billion from the sale of investments.During the year, the total in the T-account fell by $100,000 from $400,000 to $300,000. Apparently, $100,000 was the cost of the shares reissued to the public. At the same time, the capital in excess of cost balance rose from $120,000 to $160,000. That $40,000 increase in contributed capital must have been created by this sale. It would appear as investing activity because purchase of equipment impacts noncurrent assets. It represents cash inflows; in a sense, the company receives some money from the sale.Julius Mansa is a CFO consultant, finance and accounting professor, investor, and U.S. Department of State Fulbright research awardee in the field of financial technology. He educates business students on topics in accounting and corporate finance. Outside of academia, Julius is a CFO consultant and financial business partner for companies that need strategic and senior-level advisory services that help grow their companies and become more profitable. Operating activities include the production, sales and delivery of the company’s product as well as collecting payment from its customers. This could include purchasing raw materials, building inventory, advertising, and shipping the product.A cash inflow of $594,000 is reported within investing activities with a labeling such as cash received from sale of equipment. The difficulty in this process can come from having to sort through multiple purchases and sales to compute the exact amount of cash involved in each transaction. At times, determining these cash effects resembles the work required to solve a puzzle with many connecting pieces. Often, the accountant must replicate the journal entries that were made originally. Even then, the cash portion of these transactions may have to be determined by mathematical logic. To illustrate, assume that a company reports the following account balances.In the statement of cash flows for this company, the investing activities are listed as follows. Cash flow from investing is listed on a company’s cash flow statement. Cash flow from investing activities includes any inflows or outflows of cash from a company’s long-term investments. Figure 12.1 “Examples of Cash Flows from Operating, Investing, and Financing Activities” shows examples of cash flow activities that generate cash or require cash outflows within a period. It can also be useful to examine these cash flows on a trend line. When there is a steady decline in investments in fixed assets, it can imply that management does not believe there are good investment opportunities within the business. If so, there should be an increase in dividend payouts, because management has chosen to instead send excess cash back to investors.Apparently, both companies chose to return cash to owners by repurchasing stock. A section of the statement of cash flows that includes cash activities related to noncurrent assets, such as cash receipts from the sale of equipment and cash payments for the purchase of long-term investments. When a company sells any of its long-term investments or sells any of its property, plant and equipment, it is assumed to be providing or increasing the company’s cash and cash equivalents. Therefore, the cash received from the sale of these long-term assets will be reported as positive amounts in the cash flows from investing activities section of the SCF. As a result, these investments and capital expenditures are reported as negative amounts in the cash flows from investing activities section of the SCF.
