Content
- What Is Included In A Balance Sheet?
- The Income Statement
- Financial Statement Ratios And Calculations
- Income From Continuing Operations
- What Goes Into An Income Statement?
- Beginners’ Guide To Financial Statement
This leftover money belongs to the shareholders, or the owners, of the company. Liabilities also include obligations to provide goods or services to customers in the future. We all remember Cuba Gooding Jr.’s immortal line from the movie Jerry Maguire, “Show me the money! They show you where a company’s money came from, where it went, and where it is now.Selling, General and Administrative expenses (SG&A or SGA) – consist of the combined payroll costs. ScaleFactor is on a mission to remove the barriers to financial clarity that every business owner faces. Times interest earned or interest coverage ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to honor its debt payments. It may be calculated as either EBIT or EBITDA divided by the total interest payable. Pension plans and other retirement programs – The footnotes discuss the company’s pension plans and other retirement or post-employment benefit programs. The notes contain specific information about the assets and costs of these programs, and indicate whether and by how much the plans are over- or under-funded. When you subtract the returns and allowances from the gross revenues, you arrive at the company’s net revenues.In this article, we will explain four types of revenue forecasting methods that financial analysts use to predict future revenues. Learn to analyze an income statement in CFI’s Financial Analysis Fundamentals Course. Finance costs are costs of borrowing from various creditors (e.g., interest expenses, bank charges). Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts.
What Is Included In A Balance Sheet?
The purpose of MD&A is to provide investors with information that the company’s management believes to be necessary to an understanding of its financial condition, changes in financial condition and results of operations. It is intended to help investors to see the company through the eyes of management. It is also intended to provide context for the financial statements and information about the company’s earnings and cash flows. A loss happens the same way a gain does — in an unpredictable manner — but produces a negative effect on a company’s financial statements. For example, a business wants to halt the cash bleeding at a segment that has coped with competitive tedium for many quarters, preferring to jettison the losing unit and incur a one-time loss. The negative difference between the unit’s sale price and its book value flows into the “income from discontinued operations” section of the company’s statement of profit and loss. 
The Income Statement
In other words, it’s the profit before any non-operating income, non-operating expenses, interest, or taxes are subtracted from revenues. Cash flow statements report a company’s inflows and outflows of cash. This is important because a company needs to have enough cash on hand to pay its expenses and purchase assets. While an income statement can tell you whether a company made a profit, a cash flow statement can tell you whether the company generated cash. These are expenses that go toward supporting a company’s operations for a given period – for example, salaries of administrative personnel and costs of researching new products. 
Financial Statement Ratios And Calculations
Assets are generally listed based on how quickly they will be converted into cash. Current assets are things a company expects to convert to cash within one year. Most companies expect to sell their inventory for cash within one year. 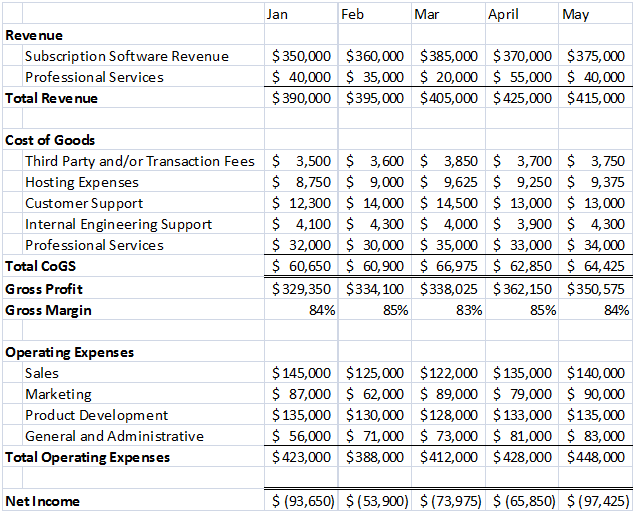
Income From Continuing Operations
It includes a company’s operations, the efficiency of its management, the possible leaky areas that may be eroding profits, and whether the company is performing in line with industry peers. Revenues realized through secondary, non-core business activities are often referred to as non-operating recurring revenues. Within the financial statement reports, the budget column displays the current or monthly budgets compared to actuals. Currently, the monthly budgets allows departments to spread their annual budget into 12 different buckets. If users do not utilize the monthly budget function and make adjustments, then the budget is spread evenly across the remaining open periods. UCO is currently evaluating including other budget options within the financial statement reports for those units who do not complete monthly budgets. Net income is the difference between revenues and expenses on the income statement.
- Net position is typically looked at on a historical and comparative basis by comparing numerous fiscal years to one another.
- The foundation of the balance sheet lies in the accounting equation where assets, on one side, equal equity plus liabilities, on the other.
- Charitable organizations that are required to publish financial statements do not produce an income statement.
- Times interest earned or interest coverage ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to honor its debt payments.
- This section discusses what makes up the income statement and how it is used internally within Indiana University.
- At the top of the income statement is the total amount of money brought in from sales of products or services.
These costs are used to fulfill goods and services IU has agreed to provide. Common examples of expenses included in COGS are cost of materials, inventory costs, and direct labor. Because of its importance, earnings per share are required to be disclosed on the face of the income statement. A company which reports any of the irregular items must also report EPS for these items either in the statement or in the notes. Cumulative effect of changes in accounting policies is the difference between the book value of the affected assets under the old policy and what the book value would have been if the new principle had been applied in the prior periods. For example, valuation of inventories using LIFO instead of weighted average method.
What Goes Into An Income Statement?
The third part of a cash flow statement shows the cash flow from all financing activities. Typical sources of cash flow include cash raised by selling stocks and bonds or borrowing from banks. Likewise, paying back a bank loan would show up as a use of cash flow. It’s the money that would be left if a company sold all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities.Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know. Whether it’s to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; people who rely on dummies, rely on it to learn the critical skills and relevant information necessary for success. What is your contribution margin and how does it compare to prior periods’ contribution margins? An entity’s contribution margin should generally be increasing from period to period. Interest expense – interest payments made on existing debt such us lines of credit, loans, etc. External debt and related expenses is typically handled by the Office of the Treasurer.
What is reported on the income statement quizlet?
An income statement reports the revenues earned less the expenses incurred by a business over a period of time. … Cash, Supplies, Prepaid insurance, Equipment, Accounts payable, Unearned Revenue, Total Liabilities, Common stock, retained earnings.Financial managers report a gain or loss in an income statement, similar to a revenue item or operating expense. An income statement also goes by the names “statement of profit and loss,” “report on income” and “P&L.” In addition to revenues and expenses, other financial accounts include assets, liabilities and equity items. An income statement is a financial statement that shows you the company’s income and expenditures. It also shows whether a company is making profit or loss for a given period. The income statement, along with balance sheet and cash flow statement, helps you understand the financial health of your business.It spent various amounts as listed for the given activities that total $10,650. It realized net gains of $2,000 from the sale of an old van, and incurred losses worth $800 for settling a dispute raised by a consumer. The above example is the simplest forms of the income statement that any standard business can generate. It is called the Single-Step Income Statement as it is based on the simple calculation that sums up revenue and gains and subtracts expenses and losses. While primary revenue and expenses offer insights into how well the company’s core business is performing, the secondary revenue and expenses account for the company’s involvement and its expertise in managing the ad-hoc, non-core activities. Recurring rental income gained by hosting billboards at the company factory situated along a highway indicates that the management is capitalizing upon the available resources and assets for additional profitability. The income statement focuses on four key items—revenue, expenses, gains, and losses.
What Is The Income Statement?
The smaller the ratio, the greater the organization’s ability to generate profit should revenues decrease. Most income statements include a calculation of earnings per share or EPS. This calculation tells you how much money shareholders would receive for each share of stock they own if the company distributed all of its net income for the period.
Balance Sheet Vs Income Statement: What’s The Difference?
Revenue is usually accounted for in the period when sales are made or services are delivered. Receipts are the cash received and are accounted for when the money is actually received. For instance, a customer may take goods/services from a company on 28 September, which will lead to the revenue being accounted for in the month of September. Owing to his good reputation, the customer may be given a 30-day payment window. It will give him time till 28 October to make the payment, which is when the receipts are accounted for. Revenue realized through primary activities is often referred to as operating revenue. For a company manufacturing a product, or for a wholesaler, distributor or retailer involved in the business of selling that product, the revenue from primary activities refers to revenue achieved from the sale of the product.Usually, investors and lenders pay close attention to the operating section of the income statement to indicate whether or not a company is generating a profit or loss for the period. Not only does it provide valuable information, but it also shows the efficiency of the company’s management and its performance compared to industry peers. Vertical analysis refers to the method of financial analysis where each line item is listed as a percentage of a base figure within the statement. This means line items on income statements are stated in percentages of gross sales, instead of in exact amounts of money, such as dollars. The operating ratio can be used to determine the efficiency of a company’s management by comparing operating expenses to net sales. It is calculated by dividing the operating expenses by the net sales.We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in oureditorial policy. After discounting for any non-recurring events, the value of net income applicable to common shares is arrived at. Microsoft had a 68% higher net income of $16.571 billion compared to Walmart’s $9.862 billion. Depreciation Expense – the allocation of the cost of a capital asset expensed over the expected life “useful life” of the asset. Some numbers depend on accounting methods used (e.g., using FIFO or LIFO accounting to measure inventory level). “If you use a cloud accounting program, it’s a living, breathing document that can be updated in near real time,” said Dennis Sherrin, a certified public accountant and past chairman of theAlabama Society of CPAs.Users must make this supporting documentation for the entity’s income statement available upon request for audit or other purposes. Documentation should be maintained for all non-system generated transactions. For further information see the Income Statement Substantiation section. Complete a variance analysis for all operating accounts on a quarterly basis. As part of this process, organizational units need to be able to provide explanations of material variances to UCO, upon request only. Please check with your campus and/or RC, as they may require variance analysis submission on a quarterly or annual basis. Run the income statement at least quarterly with comparative balances.See the Accounting Fundamentals section and Revenue Recognition section for further guidance on revenue recognition and proper recording of revenue balances. The importance of the two reports varies by reader, but the general view is that the balance sheet is second in importance to the income statement, because the income statement reports the results of the enterprise. Creditors and lenders use the balance sheet to see if a business is over-leveraged, which tells them if they should extend additional credit to the entity. They use the income statement to decide whether a business is generating a sufficient profit to pay off its liabilities.
