Content
- The Role Of Standards In Variance Analysis
- Start Your Business
- When To Use Unfavorable Variances
- “unfavorable Variance” In Spanish
- Understanding Favorable Vs Unfavorable Variance
- Variance Analysis
- What Is An Unfavorable Variance And How To Avoid It?
A company that operates with long production runs sets a low labor-cost per unit produced. Midway through the year, it switches to a pull-based manufacturing system where units are only produced if there is a customer order. In total, the company experiences a massive decline in costs, even though there is a large unfavorable labor efficiency variance that is caused by the employees working on fewer units. As mentioned above, materials, labor, and variable overhead consist of price and quantity/efficiency variances.In contrast, cost standards indicate what the actual cost of the labor hour or material should be. Standards, in essence, are estimated prices or quantities that a company will incur. When revenues are lower than expected, or expenses are higher than expected, the variance is unfavorable. For example, if the expected price of raw materials was $7 a pound but the company was forced to pay $9 a pound, the $200 variance would be unfavorable instead of favorable. If the number of classes had remained at 500, and we still saw the increase in wages, there would be more cause for concern., right? But, what if the wages had gone up, more than the increase in revenue? Each favorable and unfavorable variance needs to be examined individually, as noted in the popcorn example in the video! 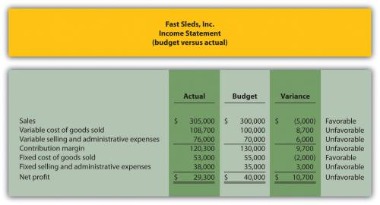
The Role Of Standards In Variance Analysis
Firstly, you may decide to adjust your budget to ensure it remains realistic. Finally, you could adjust internal processes to eliminate inefficiencies and wastage, thereby improving your bottom line.
What is an example of a unfavorable variance?
Higher than expected expenses can also cause an unfavorable variance. For example, if your budgeted expenses were $200,000 but your actual costs were $250,000, your unfavorable variance would be $50,000 or 25 percent.When the amount of actual revenue is less than the standard or budgeted amount. Thus, actual revenues of $400,000 versus a budget of $450,000 equals an unfavorable revenue variance of $50,000. Quantity standards indicate how much labor (i.e., in hours) or materials (i.e., in kilograms) should be used in manufacturing a unit of a product.Fixed overhead, however, includes a volume variance and a budget variance. Other times companies not only achieve their budgeted number, they exceed them. The difference between the actual and budgeted numbers that results in more net income than expected is considered a favorable variance. Companies with favorable variances often have spending surpluses and additional money for future periods.Favorable variance is a difference between planned and actual financial results that is in favor of the business. For example, if a business expected to pay around $100,000 for equipment maintenance, but was able to contract a price of $75,000, they’ll have a favorable variance of $25,000. It’s also important to note that budget variances are likely to be a greater issue with static budgets than they are with flexible budgets, which allow for updates and changes to be made when assumptions change. For this reason, many companies choose to use a flexible budget, rather than a static budget. Now, let’s explore favorable variances and unfavorable variances in a little more depth.
Start Your Business
It may be due to the company acquiring defective materials or having problems/malfunctions with machinery. Suppose a company expected to pay $9 a pound for 100 pounds of raw material but was able to contract a price of $7 a pound. Since the company spent less than expected, the $200 is a favorable variance. Accountants can use standard costing to identify variances in business operating statistics. Variance analysis can help a business narrow in on areas of operations that aren’t performing as they should be. 
When To Use Unfavorable Variances
This can result in the reported revenue varying greatly from the expectation of the forecasted budget. Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes. Understanding where the variance took place in your budget can help you keep track of your business tracking and accounting.The sooner these variances can be detected, the sooner management can address the problem and avoid a loss of profit. Unfavorable variances often indicate that something did not go according to plan, financially. When actual results are better than expected results given variance is described as favorable variance. In common use favorable variance is denoted by the letter F – usually in parentheses . The concept of variance is intrinsically connected with planned and actual results and effects of the difference between those two on the performance of the entity or company.
“unfavorable Variance” In Spanish
With most budgets, there is a likelihood of there being unpredictable variances. Small variances often happen when doing business, but larger variances should be investigated. A variance in your budget is often caused by improper budgeting where the baseline that has been set up has not been reasonably measured against the actual results. When actual results are worse than expected results given variance is described as adverse variance, or unfavourable variance. In common use adverse variance is denoted by the letter U or the letter A – usually in parentheses .Fixed overhead expenses tend to remain relatively stagnant, and businesses don’t usually experience significant variances in this area. However, if property tax, insurance costs, manager salaries or depreciation rose unexpectedly, it can create an unfavorable variance.
- Favorable variance is a difference between planned and actual financial results that is in favor of the business.
- Managers are then responsible for bringing the variance back into conformity with the budget.
- Budget variance is the difference between expenses and revenue in your financial budget and the actual costs.
- Suppose a company expected to pay $9 a pound for 100 pounds of raw material but was able to contract a price of $7 a pound.
- Management should only pay attention to those that are unusual or particularly significant.
- Usually, the best indicator of an unfavorable variance that requires remediation is when the baseline is historical performance, rather than an arbitrary standard.
This variance would be presented on paper as either $200 favorable or simply $200. Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. Asking yourself why a variance has occurred could help you plan your budget better. Timing variances can be reversed quickly though because when you were short in one period, you will likely be covered in the next period and eventually end up the right spot overall. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.To create a plan that can correct these variances, you have to understand what’s impacting your budget. If you don’t dig enough for these answers, you could create a fix that is targeting an incorrect area of your business that may very well cause more damage to your budget.
Understanding Favorable Vs Unfavorable Variance
Budget variance is the difference between expenses and revenue in your financial budget and the actual costs. In budgeting , a variance is the difference between a budgeted, planned, or standard cost and the actual amount incurred/sold.Combining those two lines under a supply line item can ensure that you have a favorable variance of $1,000 in your budget plan. Most companies prepare budgets to help track expenses and achieve financial performance goals. There are many different forms of budgets as well as planning strategies, but most budgets start the same way. Management analyzes the past performance of the company and estimates future performance based on expected market and economic changes. You can calculate your budget variances by subtracting the budgeted amount from the actual expenses. Then divide that number by the original budgeted amount and multiply by 100 to get the percentage of your variance.
Total Overhead Contribution & Accounting Terms
When a budget is achieved the budgeted revenue and expenses are the same as the actual revenue and expenses. Sometimes, there could be a discrepancy in your data accuracy simply because of a typo during entry. Other times the variance could be the result of something more complicated like price or volume being different from what was budgeted. This might happen when an invoice has not been received or a payment was made earlier or later than expected. If an invoice is not entered during the correct time period, it can throw off your whole monthly budget and cause unexpected variances.
Variance Analysis
Unfavorable variances are labeled as such or expressed as a negative number. This variance would be presented on paper as either $200 unfavorable, -$200 or ($200). Uncontrollable expenses most likely occur in the marketplace when a company’s supply is greater than their projected demand from customers.
What Is An Unfavorable Variance And How To Avoid It?
A budget analysis will help you consider these discrepancies in future accounting. Some expenses may not be able to be altered in the short term, but most expenses can be eliminated without impacting your company’s profits. Learn more about how you can improve payment processing at your business today.
Net Variance
The variance is unfavorable because having less actual revenues than the budgeted amount was not good for the company’s profits. It will also be one reason for the company’s actual profits being worse than the budgeted profits. Higher than expected expenses can also cause an unfavorable variance. For example, if your budgeted expenses were $200,000 but your actual costs were $250,000, your unfavorable variance would be $50,000 or 25 percent. Unfavorable budget variances refer to the negative difference between actual revenues and what was budgeted. This usually happens when revenue is lower than expected or when expenses are higher than expected.
