Content
- Software Features
- Sales
- Forecasting Financial Statements
- Step Two: Decide How Youll Make Your Forecast
- Step Three: Create Pro Forma Statements
- Construction Management
- Deliver Rolling Forecasts, Cash Flow Projections, And Scenario Planning
- Finding The Best Way To Create Financial Projections
The easiest way to create a revenue forecast is to input your annual growth rate. Look at the percentage growth in revenue over previous periods, and use that information to make an informed assumption about your future revenue. Pro forma financial statements are usually required if you need a bank loan or other form of business financing. Analysts pay close attention to accounts receivable, inventory , other current assets, property plant and equipment (PP&E), and long-term assets. While there are various approaches to forecasting a balance sheet there are some primary line items that most analysts focus on in each section of the balance sheet.Methods and lives may be specified in accounting and/or tax rules in a country. Several standard methods of computing depreciation expense may be used, including fixed percentage, straight line, and declining balance methods. Depreciation expense generally begins when the asset is placed in service. Frequently used as a way to attract future investors, financial projections are also an important component when preparing a business plan for a new business or creating a strategic plan for your current business. The best way to predict what your financial position will be is to look back at past performance. To begin building a financial statement forecast as part of your financial forecasting process, you’ll need to arm yourself with some key pieces of information from previous years. On the other hand, financial modeling is the act of taking a forecast’s assumptions and calculating the numbers using a company’s financial statements.
Software Features
Pro forma accounting is a statement of the company’s financial activities while excluding “unusual and nonrecurring transactions” when stating how much money the company actually made. If your net income plus the increase in variable liabilities equals or exceeds the increase in variable assets, the company has the resources to finance itself. 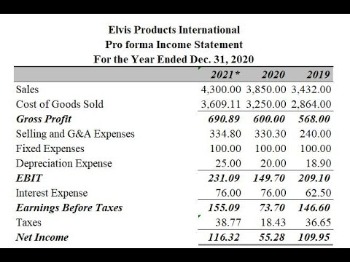
Sales
Regardless of which line item we choose to forecast, the method is simple. Most of the time, the simple percentage of sales revenue method will suffice.It becomes necessary to get into the habit of projecting income statement line items. Being able to project the main line items of the income statement should become second nature.Once you’ve collected the information you need to build your forecast, you can create pro forma statements. When you use your financial history to plot the future, it’s historical forecasting. You’re looking at your last few annual Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements, and Balance Sheets to see how fast you’ve grown in the past.
Forecasting Financial Statements
A financial forecast is an estimate of future financial outcomes for a company. Often, the forecaster’s own assumptions and beliefs will be used to guess future growth rates and potential events that will affect the numbers on a financial statement. Financial projections are an important part of managing your business. Preparing financial projections may seem like a daunting task for small business owners, but if you can create financial statements, you can create financial projections. Similar to creating a budget, financial projections are a way to forecast future revenue and expenses for your business.
How do you forecast accounts receivable on a balance sheet?
Using the formula for their respective days outstanding, we can forecast future accounts receivables, inventory, and accounts payables. The following are the formulas for annual days outstanding: Accounts Receivable Days = Average AR / Sales Revenue x 365. Inventory Days = Average Inventory / Cost of Goods Sold x 365.To accurately forecast your company’s profits or losses, you’ll first need to understand its past performance and use that data to predict future financial outcomes. If you’re developing a pro forma income statement for a one-year period beginning January 1, 2020, you’ll want to look at historical data from the same period in previous years. Best practices suggest analyzing at least two periods worth of historical data, so you would want to look at income statements from January 1, 2018 and January 1, 2019.
Step Two: Decide How Youll Make Your Forecast
Capacity utilization is a concept in economics and managerial accounting that refers to the extent to which an enterprise or a nation actually uses its installed productive capacity. Therefore, it refers to the relationship between actual output that ‘is’ produced with the installed equipment and the potential output which ‘could’ be produced with it, if capacity was fully used. Implicitly, the capacity utilization rate is also an indicator of how efficiently the factors of production are being used. Much statistical and anecdotal evidence shows that many industries in the developed capitalist economies suffer from chronic excess capacity. Therefore, critics of market capitalism argue the system is not as efficient as it may seem, since at least 1/5 more output could be produced and sold, if buying power was better distributed. 
Step Three: Create Pro Forma Statements
The only change is to add the required profit target to the fixed costs. Net sales are operating revenues earned by a company for selling its products or rendering its services.
- Conduct a contribution analysis to determine if your strategies positively contribute to the bottom line.
- Circularity is problematic in Excel, and that’s why analysts often use beginning debt balances instead.
- This means that revenue for each year will depend on a regression formula based on historic sales revenue and the input of that year’s GDP .
- Therefore, it refers to the relationship between actual output that ‘is’ produced with the installed equipment and the potential output which ‘could’ be produced with it, if capacity was fully used.
- However, if sales are to increase, the resulting expenses to produce the additional sales would also increase.
- If you’re creating a quick forecast for your own planning, you may only need to create pro forma Income Statements.
Unlike a financial plan or a budget, a financial forecast doesn’t have to be used as a planning document. Outside analysts can use a financial forecast to estimate a company’s success in the coming year. The last step in completing your financial projection is the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement ties into both the income statement and the balance sheet, displaying any cash or cash-related activities that affect your business. This analysis provides you with a projection of whether your strategy generates revenues in excess of expenses. If the contribution analysis determines that the dollar investment in the strategy required to reach this target customer group can’t be justified, rethink and adjust customer goals and financial goals.These potential outcomes can then be used to plot a company’s future path based on the highest possible degree of financial and risk certainty. This information may be used to drive cash flow and inform pro forma financial statements, which include a balance sheet, cash flow statement and income statement.Again, we can use historical figures or trends to forecast future gross margin. However, it is advised to take a more detailed approach, considering factors such as the cost of input, economies of scale, and learning curve. This second approach will allow your model to be more realistic, but also make it harder to follow. On the other hand, the quick and dirty approach to robust models outlines how you can model revenues in a much more straightforward way, with the benefit that the model will be more simple and easy to use .Basic reasons for keeping an inventory involve time, uncertainty and economics of scales. Production schedule can be divided into raw materials, work in process, finished goods and goods for resale. Fees for services are recorded separately from sales of merchandise, but the bookkeeping transactions for recording sales of services are similar to those for recording sales of tangible goods. Capacity utilization is a concept in economics and managerial accounting which refers to the extent to which an enterprise or a nation actually uses its installed productive capacity.The most straightforward method of forecasting depreciation is the Straight-Line Method. For small business accounting, depreciation is used to allocate the cost of a purchased asset over its useful lifetime.
Finding The Best Way To Create Financial Projections
Income tax expense – sum of the amount of tax payable to tax authorities in the current reporting period (current tax liabilities / tax payable) and the amount of deferred tax liabilities . Cost of goods sold refer to the inventory costs of the goods a business has sold during a particular period.
