Content
- Methods Of Depreciation & Amortization
- Comments: Amortization Vs Depreciation
- Difference Between Depreciation Vs Amortization
- What Is The Meaning Of Depreciation?
- Difference Between Depreciation And Amortization With Table
- What Is Amortization?
Fixed assets refers to the assets, whose benefit is enjoyed for more than one accounting period. Fixed assets can be tangible fixed assets or intangible fixed assets. As per matching concept, the portion of asset employed for creating revenue, needs to be recovered during the financial year, so as to match the expenses for the period. And for this purpose, depreciation and amortization is applied, on the fixed assets. Depreciation is applicable to assets such as plant, building, machinery, equipment or any tangible fixed assets. However, amortization is applicable to intangible assets such as copyrights, patent, collection rights, brand value etc.Amortization is commonly calculated using the straight-line method. Intangible assets annual amortization expenses reduce its value on the balance sheet and therefore reduced the amount of total assets in the assets section of a balance sheet. This occurs until the end of the useful lifecycle of an intangible asset. Intangible assets are non-physical assets that are essential to your business. Customer relationships, contracts, franchises, patents, and licenses are all examples of intangible assets—they’re business assets that have no material substance but that add value to your business. Depreciation is the reduction in value of a tangible asset with the passage of time, usually to account for wear and tear.
Methods Of Depreciation & Amortization
Any tangible assets over the safe harbor limit and certain types of intangible assets will still need to be capitalized and depreciated per IRS regulations. Depreciation can be used as a straight-line method or accelerated depreciation method. Accelerated depreciation is used to show higher expenses in the initial years of the erection of a machine or a building or a piece of equipment. When a business spends money to acquire an asset, this asset could have a useful life beyond the tax year. Such expenses are called capital expenditures and these costs are “recovered” or “written off” over the useful life of the asset. If the asset is intangible; for example, a patent or goodwill; it’s called amortization. 
Comments: Amortization Vs Depreciation
Specifically, amortization occurs when the depreciation of an intangible asset is split up over time, and depreciation occurs when a fixed asset loses value over time. It also added the value of Milly’s name-brand recognition, an intangible asset, as a balance sheet item called goodwill. Amortization is a method of measuring the loss in the value of long-term fixed intangible assets due to the passage of time, to know about their decreased worth is known as amortization. Long term fixed intangible assets are the assets which are owned by the entity for more than three years, but they do not exist in its material form like computer software, license, franchises, etc. Similarly, like depreciation, the amount of amortization is also shown on the assets side of the Balance Sheet as a reduction in the intangible asset. Depreciation only applies to tangible assets, like buildings, machinery and equipment, while amortization only applies to intangible assets, like copyrights and patents.These two are often identical terms and are commonly used interchangeably, but they are both governed by different accounting standards. Amount payable on the monthly basis since it does not fully amortize over the term of the loan due to its large amount then it is known as balloon payment. Depreciation can be calculated in one of several ways, but the most common is straight-line depreciation that deducts the same amount over each year. To calculate depreciation, begin with the basis, subtract the salvage value, and divide the result by the number of years of useful life. This has a been a guide to the top difference between Depreciation vs Amortization. 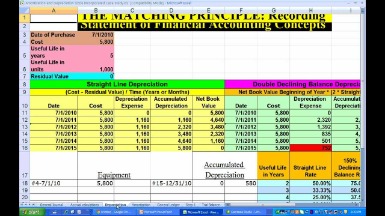
Difference Between Depreciation Vs Amortization
Long term fixed tangible assets mean the assets which are owned by the company for more than three years, and they can be seen & touched. The depreciation is charged as a capital expenditure against the revenue generated from the asset during the year i.e. matching concept. Depreciation and amortisation both meant to reduce the value of the asset year by year, but they are not one and the same thing.Salvage Value means the value obtained when the asset is resold at the end of its lifetime. Another definition of amortization is the process used for paying off loans.
Is amortization good or bad?
At its core, loan amortization helps you budget for large debts like mortgages or car loans. It’s also a useful tool to demonstrate how borrowing works. By understanding your payment process up front, you can see that sometimes lower monthly installments can result in larger interest payments over time, for example.As an example, suppose in 2010 a business buys $100,000 worth of machinery that is expected to have a useful life of 4 years, after which the machine will become totally worthless . In its income statement for 2010, the business is not allowed to count the entire $100,000 amount as an expense. Instead, only the extent to which the asset loses its value is counted as an expense.
What Is The Meaning Of Depreciation?
They would say that the company should have added the depreciation figures back into the $8,500 in reported earnings and valued the company based on the $10,000 figure. For the past decade, Sherry’s Cotton Candy Company earned an annual profit of $10,000. One year, the business purchased a $7,500 cotton candy machine expected to last for five years.
How does depreciation expense differ from other operating expenses?
Since the asset is part of normal business operations, depreciation is considered an operating expense. However, depreciation is one of the few expenses for which there is no associated outgoing cash flow. … Thus, depreciation is a non-cash component of operating expenses (as is also the case with amortization).The Section 179 election amount is calculated in Part I and bonus depreciation is calculated in Part II. You must add this form to your other business tax forms or schedules when preparing your business taxes. A home business can deduct depreciation expenses for the part of the home used regularly and exclusively for business purposes. When you calculate your home business deduction, you can include depreciation if you use the actual expense method of calculating the tax deduction, but not if you use the simplified method. Taxation advantage is more significant in the case of depreciation in comparison to amortization as an accelerated method of depreciation can be used in case of tangible assets. Both tangible and intangible assets are subject to impairment, which means that their carrying amounts can be written down. If so, the remaining depreciation or amortization charges will decline, since there is a smaller remaining balance to offset. Amortization assets cannot get any benefit from the salvage value as it cannot be resold.An amortization schedule is used to calculate a series of loan payments of both the principal and interest in each payment as in the case of a mortgage. So, the word amortization is used in both accounting and in lending with completely different definitions. Understanding depreciation and amortization is not easy and is most often best left to the professionals. IRS Publication 946 outlining all the details is hundreds of pages long—not exactly something we would expect you to read. For 2018 the maximum allowed depreciation under Section 179 of the tax code is $1,000,000 on up to $2.5 million in purchases.
Difference Between Depreciation And Amortization With Table
The safe harbor allows taxpayers to set a capitalization threshold so all amounts that fall below that number are not capitalized for federal tax reporting purposes. When amortizing an asset, the goal is to match the expense of acquiring that asset with the revenue that asset generates. They both have to be incurred for the successful running of a business cycle. The role played by both in the industry requires knowledgeable auditors and account personnel to work on the numbers. After all, taxation is connected to the government, and producing the right papers for the cost incurred must be legitimate. It represents the amount of assets’ value has been used every year. The assets which depreciate, of course, earn revenue and a part of the revenue is allocated as a cost to maintain the asset to produce revenue the next year too.Here we also discuss the Depreciation vs Amortization key differences with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.
- No business can run without owning an asset as the asset generates economic returns and revenue for the business over the life of the asset.
- The Section 179 election amount is calculated in Part I and bonus depreciation is calculated in Part II. You must add this form to your other business tax forms or schedules when preparing your business taxes.
- Understanding depreciation and amortization is not easy and is most often best left to the professionals.
- Depreciation can be calculated in one of several ways, but the most common is straight-line depreciation that deducts the same amount over each year.
- The two cost-recovery options are depreciation and amortization.
- Business assets are property owned by a business that is expected to last more than a year.
Value investors and asset management companies sometimes acquire assets that have large upfront fixed expenses, resulting in hefty depreciation charges for assets that may not need a replacement for decades. This results in far higher profits than the income statement alone would appear to indicate. Firms like these often trade at high price-to-earnings ratios, price-earnings-growth ratios, and dividend-adjusted PEG ratios, even though they are not overvalued.Non-cash ChargesNon-cash expenses are those expenses recorded in the firm’s income statement for the period under consideration; such costs are not paid or dealt with in cash by the firm. Since amortization doesn’t deal with physical assets, the process is no different for a home business than any other business that owns intangible property. However, Depreciation can be more useful for taxation purpose as a company can use accelerated depreciation to show higher expenses in initial years. Expensing a fixed asset over its useful lifecycle is called depreciation.It is the strategy to work under the law to look at these benefits which are on offer. While tangible assets are required for generating revenue, intangible assets are required for security and market branding. Capital expenses are either amortized or depreciated depending upon the type of asset acquired through the expense. Tangible assets are depreciated over the useful life of the asset whereas intangible assets are amortized.In other words, the depreciated amount expensed in each year is a tax deduction for the company until the useful life of the asset has expired. The practice of spreading an intangible asset’s cost over the asset’s useful lifecycle is called amortization.
What Is Amortization?
If you own a business, “depreciation” and “amortization” are words that may come up during that conversation. While most people have a basic understanding of depreciation, amortization is a bit more confusing. It’s similar to depreciation, and it works like depreciation…but it’s used for different kinds of business assets.Although the company reported earnings of $8,500, it still wrote a $7,500 check for the machine and has only $2,500 in the bank at the end of the year. Tangible AssetsAny physical assets owned by a firm that can be quantified with reasonable ease and are used to carry out its business activities are defined as tangible assets. For example, a company’s land, as well as any structures erected on it, furniture, machinery, and equipment. To the expenses of an asset which are fixed and are tangible. The assets are physical assets that are reduced each year due to the wear and tear in them. Most businesses file IRS Form 4562 Depreciation and Amortization to do the calculations for depreciation and amortization for the year. The information for all property depreciated and amortized is accumulated and totaled on this form.
How Does Depreciation And Amortization Work For A Home Business?
Depreciation can be used as a Straight-Line Method or accelerated depreciation method whereas AMortization can be used as a straight line method only. Amortization is the reduction of cost for the intangible items over its life span. Amortization applies to patents, licenses, rental agreements, copyrights.
Related Differences
The recovery period is the number of years over which an asset may be recovered. In this article, we define depreciation and amortization, explain how they differ and offer examples of these two accounting methods. Both depreciation and amortization are used in the finance industry for accounting and tax purposes. Depreciation is used to distribute and expense out the cost of Tangible Asset over its useful life. However, Amortization is used to expense out the value of Intangible assets over its useful life. Both depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses – that is, the company does not suffer a cash reduction when these expenses are recorded. Amortization is the cost allocation of an intangible asset over time.This will be useful for planning in certain years where you don’t need any additional expenses to have no taxable liability at year end. There are many nuances and regulations regarding this—be sure to reach out to us or your CPA to discuss the details. When you meet with your CPA, be sure to ask how they want you to determine whether an asset should be capitalized and depreciated versus expensed. Ask if they have filed or plan to file a de minimis safe harbor election form with your timely filed tax return. As a basic rule-of-thumb, you depreciate tangible assets and amortize intangible assets.
